What is minikube?
Minikube is an open-source tool that facilitates the setup and management of a single-node Kubernetes cluster on a local machine. Kubernetes is a powerful container orchestration platform used for automating the deployment, scaling, and management of containerized applications. Minikube allows developers and operators to run a Kubernetes cluster on their laptops or desktops, providing a convenient and lightweight environment for testing and development purposes.
Key features of Minikube include:
Local Kubernetes Cluster: Minikube sets up a single-node Kubernetes cluster on your local machine, enabling you to deploy and manage containers just like you would in a larger, production-scale Kubernetes environment.
Ease of Use: Minikube is designed to be user-friendly and easy to install. It simplifies the process of getting started with Kubernetes, making it accessible to developers who want to experiment with containerized applications.
Isolation: Since Minikube runs a single-node cluster on your local machine, it provides a controlled and isolated environment for testing applications. This is particularly useful for developers who want to avoid potential conflicts with other environments or dependencies.
Supported Hypervisors: Minikube supports various hypervisors, including VirtualBox, VMware, Hyper-V, and KVM. This flexibility allows users to choose the virtualization technology that best fits their system and preferences.
Add-ons and Extensions: Minikube supports various add-ons and extensions that enable users to customize their local Kubernetes cluster with additional features, such as a container registry, dashboard, and more.
Developers often use Minikube for tasks like:
Testing applications locally before deploying them to a production Kubernetes cluster.
Experimenting with different Kubernetes features and configurations in a controlled environment.
Learning and getting hands-on experience with Kubernetes without the need for a cloud-based or on-premises infrastructure.
Keep in mind that while Minikube is suitable for local development and testing, it may not fully replicate the complexities of a multi-node production Kubernetes cluster. For more realistic testing scenarios, users might consider using tools like kind (Kubernetes IN Docker) or other local cluster solutions.
Features of minikube:
Minikube is a versatile tool that comes with several features to support local Kubernetes development and testing. Here are some key features of Minikube:
Local Kubernetes Cluster: Minikube allows you to set up and run a single-node Kubernetes cluster on your local machine, providing an environment for testing and development purposes.
Multiple Hypervisor Support: Minikube supports various hypervisors, including VirtualBox, VMware, Hyper-V, and KVM. This flexibility enables users to choose the virtualization technology that best fits their system and preferences.
Cross-Platform Compatibility: Minikube is designed to work on multiple operating systems, such as Linux, macOS, and Windows, making it accessible to a wide range of developers.
Easy Installation: Minikube is easy to install and set up, with a straightforward command-line interface. This simplicity helps developers quickly create a local Kubernetes environment without dealing with complex configurations.
Isolation and Control: By running a single-node cluster locally, Minikube provides isolation for testing and development, allowing users to experiment with Kubernetes features without affecting other environments or dependencies.
Addon Management: Minikube supports various add-ons that extend the functionality of the local Kubernetes cluster. Users can enable or disable add-ons to customize their development environment. Examples of add-ons include the Kubernetes Dashboard, storage provisioners, and Ingress controllers.
Dashboard Integration: Minikube includes integration with the Kubernetes Dashboard, a web-based user interface for managing and monitoring Kubernetes clusters. This makes it easier for developers to visualize and interact with their local cluster.
Node Customization: Users can customize Minikube's virtual machine (VM) settings, such as CPU and memory allocations, to match their application's requirements or to simulate different environments.
Container Runtime Support: Minikube supports different container runtimes, allowing users to choose between Docker, containerd, and others based on their preferences or project requirements.
Automatic Updates: Minikube can automatically check for updates and upgrade the Kubernetes cluster to the latest stable version, ensuring that developers have access to the latest features and improvements.
Networking Options: Minikube provides options for configuring network settings, including using a custom or existing network, to accommodate various network setups and requirements.
Minikube is a valuable tool for developers and teams looking to set up a local Kubernetes environment for testing, learning, and development purposes. Its ease of use, flexibility, and compatibility with different platforms make it a popular choice in the Kubernetes ecosystem.
Install minikube on your local:
How to install minikube in AWS EC2 Ubuntu Machine:
Login to AWS Console:
Go to the AWS Management Console (https://aws.amazon.com/).
Sign in with your AWS account.
Navigate to EC2:
In the AWS Management Console, navigate to the EC2 service.
Launch an Instance:
Click on the "Instances" in the left navigation pane.
Click the "Launch Instances" button.
Choose an Amazon Machine Image (AMI):
In the "Step 1: Choose an Amazon Machine Image (AMI)" section, select an Ubuntu AMI. You can search for "Ubuntu" in the search bar and choose an appropriate version (e.g., Ubuntu Server 20.04 LTS).
Choose an Instance Type:
In the "Step 2: Choose an Instance Type" section, select "t2.xlarge" as the instance type.
Click "Next: Configure Instance Details."
Configure Instance Details:
In the "Step 3: Configure Instance Details" section:
Set the "Number of instances" to 1.
Optionally, you can configure additional settings, such as network, subnet, IAM role, etc.
Click "Next: Add Storage."
Add Storage:
In the "Step 4: Add Storage" section, you can leave the default storage settings or adjust as needed.
Click "Next: Add Tags."
Add Tags:
In the "Step 5: Add Tags" section, click "Add Tag."
For "Key," enter "Name" and for "Value," enter "Jenkins" (or your preferred name).
Click "Next: Configure Security Group."
Configure Security Group:
In the "Step 6: Configure Security Group" section:
Create a new security group or use an existing one.
Add inbound rules to allow HTTP (port 80), HTTPS (port 443), and SSH (port 22) traffic.
Click "Review and Launch."
Review and Launch:
Review your configuration settings.
Click "Launch."
Select Key Pair:
In the key pair dialog, select "Choose an existing key pair" and choose the "minikube" key pair.
Acknowledge that you have access to the private key.
Click "Launch Instances."
View Instances:
Once the instance is launched, you can view it in the EC2 dashboard.
Wait for the instance to reach the "running" state.
Setup minikube in Ubuntu:
Go to Ubuntu Machine and update the ubuntu machine:
sudo apt-get update
curl -LO https://storage.googleapis.com/minikube/releases/latest/minikube-linux-amd64
sudo install minikube-linux-amd64 /usr/local/bin/minikube
minikube start
sudo apt-get install docker.io
sudo usermod -aG docker $USER && newgrp docker
sudo reboot
minikube start
minikube start --driver=docker
sudo snap install kubectl --classic
kubectl get po -A
How to Setup Minikube in Ubuntu Machine Live:
Launching your First Kubernetes Cluster with Nginx running:
Create Nginx Pod:
kubectl run my-nginx --image=nginx:latest

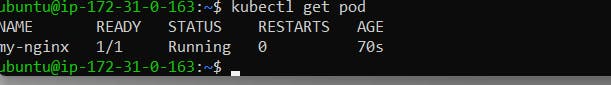
Now my-nginx name pod is running
