Introduction:
Greetings to the uncharted territory of DevOps, where the synergy of clever strategies and teamwork orchestrates a revolution in how businesses shape and launch software. In this blog post, we're embarking on a journey through the fascinating world of DevOps, demystifying its complexities with everyday examples to help those not immersed in the tech world comprehend its significance for organizations. Buckle up for an exhilarating ride as we explore DevOps in straightforward terms, unraveling its concepts and unveiling the pivotal role it plays in the success of businesses.
What is DevOps:
DevOps is not a software also It is not a technology. It is a Methodology. There are three methodology, Waterfall Methodology, Agile Methodology and Devops
So DevOps is improvement of Agile Methodology.
DevOps is combination of two words i.e. development and operation.
DevOps is Software Development approach which involves Continuous Development, Continuous Testing, Continuous Integration and Continuous Monitoring of the software throughout its development lifecycle.
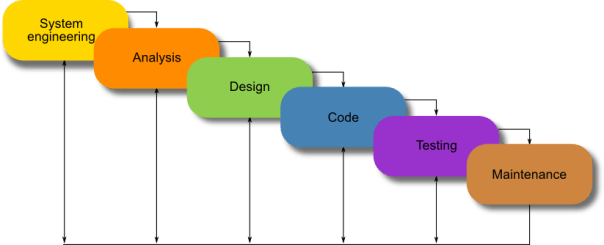
Waterfall Model:
The Waterfall Model is a traditional software development methodology that follows a linear and sequential approach. It consists of several distinct phases, and each phase must be completed before moving on to the next.
Architecture of waterfall model:
Advantages of waterfall model:
Stability in Project Scope:
The project scope remains relatively constant, allowing for early determination of costs and timelines. This stability is beneficial for project planning and budgeting.
Cost-Effective Design Changes:
Completing a full design early in the project minimizes changes to systems. This helps in keeping the cost and effort required to fix or alter designs at a minimum, as modifications are less likely to occur.
Structured Project Approach:
The Waterfall model provides a structured and sequential approach to project development. This clarity ensures that everyone involved understands what tasks need to be performed and when, facilitating effective planning and execution.
Effective Time Planning for SMEs:
Subject Matter Experts (SMEs) can efficiently plan their time over the fixed project duration due to the well-defined stages and timeline. This predictability contributes to better resource management.
Documentation for Knowledge Transfer:
Detailed documentation and designs accompany each phase of the Waterfall model. This documentation serves as a valuable resource, allowing the project to continue smoothly even if key team members are replaced or reassigned.
Disadvantages of waterfall model:
Limited Flexibility for Changes:
One of the major drawbacks is the lack of flexibility once the project has started. Changes in requirements or design are challenging to implement once a phase has been completed, potentially leading to an unsatisfactory end product if initial requirements were not well-defined.
Late Client Feedback:
Client or user feedback is typically gathered late in the process, usually after the entire system has been developed. This can result in situations where client expectations are not fully met, as changes based on feedback are challenging to incorporate in the later stages of development.
Long Delivery Time:
The Waterfall model follows a sequential approach, completing one phase before moving to the next. This can lead to longer delivery times, especially for large and complex projects, as each phase must be fully completed before proceeding to the next.
Risk of Ambiguous Requirements:
In the initial stages, if requirements are not thoroughly defined or are ambiguous, it can lead to misunderstandings and misinterpretations. This may result in a final product that does not meet the actual needs of the users.
High Dependency on Initial Documentation:
The success of the Waterfall model heavily relies on comprehensive documentation. If the initial documentation is incomplete or inaccurate, it can lead to misunderstandings and errors throughout the project lifecycle.
Inefficient for Large Projects:
For large and complex projects, the Waterfall model may not be the most efficient choice. The lengthy development process may result in delayed detection of issues, making it challenging to address them in a timely manner.
Limited Customer Involvement:
Customers are typically involved at the beginning and end of the project, with limited interaction during the development phases. This reduced customer involvement may lead to a final product that does not fully align with customer expectations.
Not Suitable for Evolving Requirements:
In dynamic environments where requirements are likely to change, the Waterfall model may not be the best fit. It does not handle evolving or uncertain requirements well, as changes are difficult to accommodate once the project is in progress.
Agile Methodology:
Agile is an iterative and flexible software development methodology that focuses on delivering small, incremental releases of a product with continuous feedback and adaptation to changes.
Architecture of Agile model:
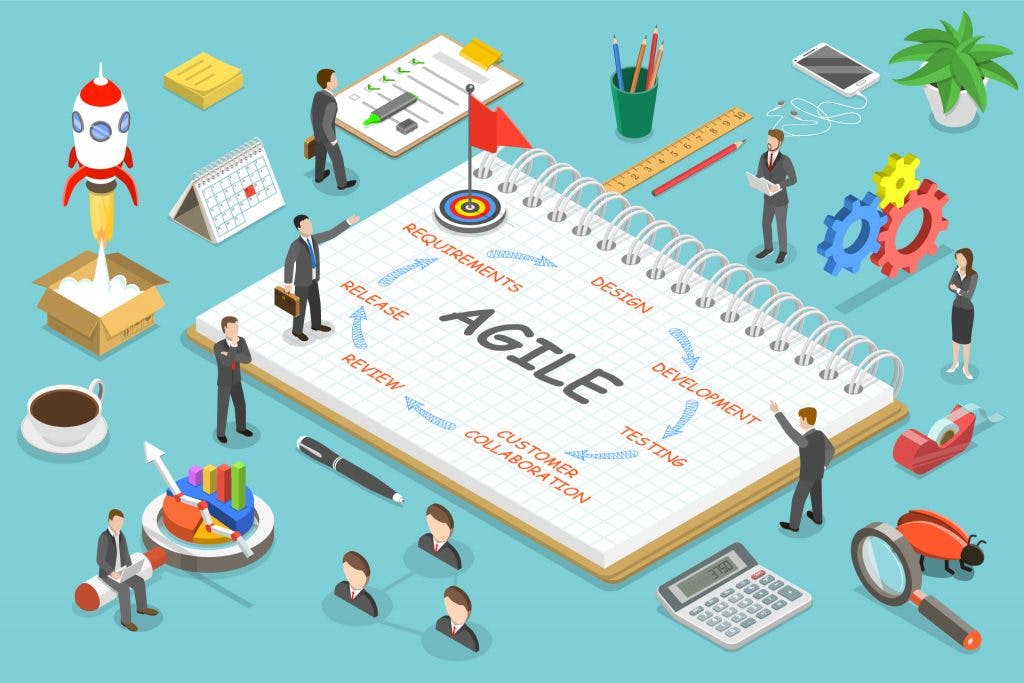

Advantages of Agile model:
Flexibility to Change:
- Advantage: Agile embraces changes in requirements even late in the development process, allowing teams to respond quickly to evolving needs in real-time.
Continuous Delivery:
- Advantage: Agile promotes the delivery of a working product in short iterations, enabling real-time feedback and regular releases, which can be crucial for fast-paced industries.
Enhanced Collaboration:
- Advantage: Agile methodologies emphasize collaboration among cross-functional teams, ensuring real-time communication and coordination between developers, testers, and other stakeholders.
Customer Satisfaction:
- Advantage: Regular demonstrations and feedback loops allow stakeholders to provide real-time input, ensuring that the final product aligns with customer expectations and needs.
Quick Problem Identification:
- Advantage: With frequent testing and delivery, issues and challenges can be identified early in the development process, enabling real-time problem-solving and adjustments.
Adaptation to Market Changes:
- Advantage: Agile enables teams to respond promptly to changes in the market or industry, ensuring that the product remains relevant and competitive in real-time.
Improved Risk Management:
- Advantage: Incremental development and continuous testing help in identifying and mitigating risks in real-time, reducing the likelihood of major project setbacks.
Disadvantages of Agile model:
Requires Strong Collaboration:
- Disadvantage: Agile relies heavily on effective collaboration and communication. In real-time environments where teams are geographically dispersed or communication is challenging, maintaining this collaboration can be a challenge.
Continuous Client Involvement:
- Disadvantage: Agile requires active and continuous involvement from stakeholders. In real-time environments where clients or key stakeholders are not readily available, this may hinder the effectiveness of the Agile approach.
Documentation Challenges:
- Disadvantage: Agile values working software over comprehensive documentation. In real-time environments where detailed documentation is crucial, teams may face challenges in ensuring that necessary documentation is up to date.
Complexity in Large Projects:
- Disadvantage: While Agile is well-suited for small to medium-sized projects, it may face challenges in managing complexity and scaling for large projects in real-time environments.
Potential for Scope Creep:
- Disadvantage: Without proper control, Agile projects can be susceptible to scope creep, where new requirements are continuously added. This can lead to challenges in managing timelines and budgets in real-time.
Resource Dependency:
- Disadvantage: Agile requires skilled and committed team members. In real-time environments where team members may have other competing priorities, maintaining the necessary level of commitment can be challenging.
Importance of Devops ?
Imagine DevOps as the smooth coordination and collaboration between the construction team and the decorators when building your dream house. DevOps is crucial because it's like having the right team of experts working seamlessly together to make sure your house not only gets built but also looks fantastic inside and out.
Here's why DevOps is so important in a simple:
Faster House Building (or Software Delivery):
- DevOps makes the process of building and delivering software faster. It's like having a team that knows how to work efficiently, so your software is ready in no time.
Fewer Mistakes, More Beautiful Results:
- Just like you want your house to be perfect, DevOps ensures that the software comes out with fewer mistakes. It's like having a team that pays attention to every detail, so your software works smoothly and looks great.
Everyone Working Together Like a Dream Team:
- DevOps brings different experts together, just like how you'd want your electricians, plumbers, and painters to work seamlessly on your house. This collaboration ensures that every part of the software gets the attention it needs.
Fixing Problems Before They Become Big Issues:
- DevOps is like having a team that regularly checks your house for any issues and fixes them before they become major problems. In software, this means identifying and fixing any bugs before they cause trouble.
Keeping Things Up-to-Date and Trendy:
- DevOps makes sure your software is always up-to-date, just like you'd want the interior of your house to be trendy. It ensures that your software keeps up with the latest and greatest features.
Less Stress, More Enjoyment:
- With DevOps, the process is smoother, and there's less stress. It's like having a team that takes care of everything, allowing you to enjoy the benefits of your new software without worrying about how it was made.
In a nutshell, DevOps is like having a fantastic team of builders and decorators for your software, ensuring it's built quickly, looks amazing, and functions perfectly – making your digital experience a joy!
Architecture of DevOps.

Popular DevOps Tools.

Automation, Scaling, Infrastructure.
In real-time scenarios, Automation, Scaling, and Infrastructure play crucial roles in the world of DevOps. Let's break down these concepts in a more practical sense:
Automation:
Real-Time Example: Continuous Integration/Continuous Deployment (CI/CD)
Imagine you're a chef cooking in a busy restaurant kitchen. Instead of manually chopping vegetables, measuring ingredients, and cooking each dish separately, you have a set of automated kitchen tools. These tools help you streamline the cooking process – chopping, measuring, and cooking at the push of a button. In DevOps, automation is like setting up pipelines that automatically build, test, and deploy software changes. It's like having a well-organized kitchen where each step of the process is automated, ensuring that software updates are efficiently delivered without errors.
Scaling:
Real-Time Example: Handling Increased Website Traffic
Suppose you own an online store, and suddenly there's a surge in customers wanting to buy your products. Scaling in DevOps is similar to quickly and seamlessly accommodating this increased demand. It's like hiring more staff, opening additional checkout counters, and ensuring your website can handle the extra traffic without slowing down. In real-time DevOps, scaling means dynamically adjusting resources to meet the demands of your software application. It ensures that your systems can handle both regular and peak workloads efficiently.
Infrastructure:
Real-Time Example: Cloud Computing
Think of infrastructure as the foundation of your business. In a real-time DevOps scenario, using cloud services is like having a flexible and scalable foundation for your software. It's like renting additional kitchen space for a big event instead of building a new kitchen. Cloud infrastructure allows you to easily scale resources up or down based on demand, just like adjusting the size of your kitchen depending on the number of customers. It provides the necessary servers, storage, and networking components without the need for physical hardware.
Integration in Real-Time:
Now, let's bring it all together in a real-world example:
Imagine you have an e-commerce website. Automation ensures that whenever there's a change in the product catalog or website code, it automatically goes through testing and deployment. Scaling comes into play during special events or promotions when the website experiences a sudden increase in visitors. The infrastructure, supported by cloud services, dynamically allocates additional servers and resources to handle the increased traffic.
In real-time DevOps, this cohesive integration of Automation, Scaling, and Infrastructure ensures that your software delivery is efficient, adaptable to varying workloads, and supported by a robust technological foundation. It's like running a restaurant kitchen where automated processes, quick scalability, and a reliable infrastructure work together to serve your customers seamlessly.
Interview Questions in DevOps:
What is DevOps.
Which one is better (Waterfall Methodology, Agile Methodology and DevOps).
Automation, Scaling and Infrastructure.
Conclusion: DevOps represents a winning strategy that empowers businesses to enhance their software development and deployment practices. Through fostering collaboration, implementing automation, and embracing scalability, organizations can optimize their workflows, expedite product launches, and establish robust and dependable software systems. Embracing the transformative capabilities of DevOps unlocks unparalleled efficiency and growth prospects for any enterprise. Embark on an exhilarating journey of learning and skill development, where you not only elevate your personal knowledge but also contribute to the empowerment of others in the realm of DevOps with Shubham Londhe .
